|
Johan Mathé has spent the past 15 years applying AI to the hardest problems in physics: systems where uncertainty, nonlinearity, and chaos are not bugs but defining features. As one of the early Google and Google X employees, Johan led core AI systems for autonomous high-altitude aircraft as part of Project Loon, pushing learning-based control into real-world, safety-critical flight. He then joined the founding team of Caption Health, where he co-designed the first FDA-approved AI guidance system for ultrasound—technology that brought expert-level medical imaging to non-experts and was later acquired by GE Healthcare. Caption's AI platform was recognized as a TIME Best Invention of the Year. From medicine, Johan moved to space: applying physics-informed machine learning to magnetohydrodynamics and electric propulsion, contributing to next-generation Hall-effect thrusters for spacecraft. Five years ago, Johan founded Atmo, pioneering AI-based weather forecasting at national scale. Atmo became the first private company to deploy AI weather models operationally for entire nations (including the Philippines, one of the countries most exposed to typhoons and climate-driven extreme weather) as well as for U.S. defense agencies such as the Navy and Air Force. These systems continuously inform real-world decisions, making Atmo one of the first AI deployed systems at scale with the explicit purpose of mitigating climate change in practice. Beyond forecasting, Atmo develops AI algorithms for weather modification and atmospheric intervention, aimed at optimizing targeted, physics-constrained influence on extreme events. Atmo's work was named a TIME Best Invention of the Year in 2024. Across aviation, medicine, space, and climate, Johan's work centers on learning in chaotic systems. He holds 14 patents, has published at NeurIPS, and maintains multiple open-source projects. Outside of his formal work, he actively fosters a Bay Area community of builders and tinkerers. He argues that chaos theory places fundamental limits on prediction and control—limits that challenge singularity narratives and frame AI not as an inevitable takeover force, but as a powerful tool for navigating irreducible uncertainty. Email / LinkedIn / Github / Google Scholar |

|
|
Interest in signal processing, optimization, statistics/machine learning, image processing and control theory. |
|
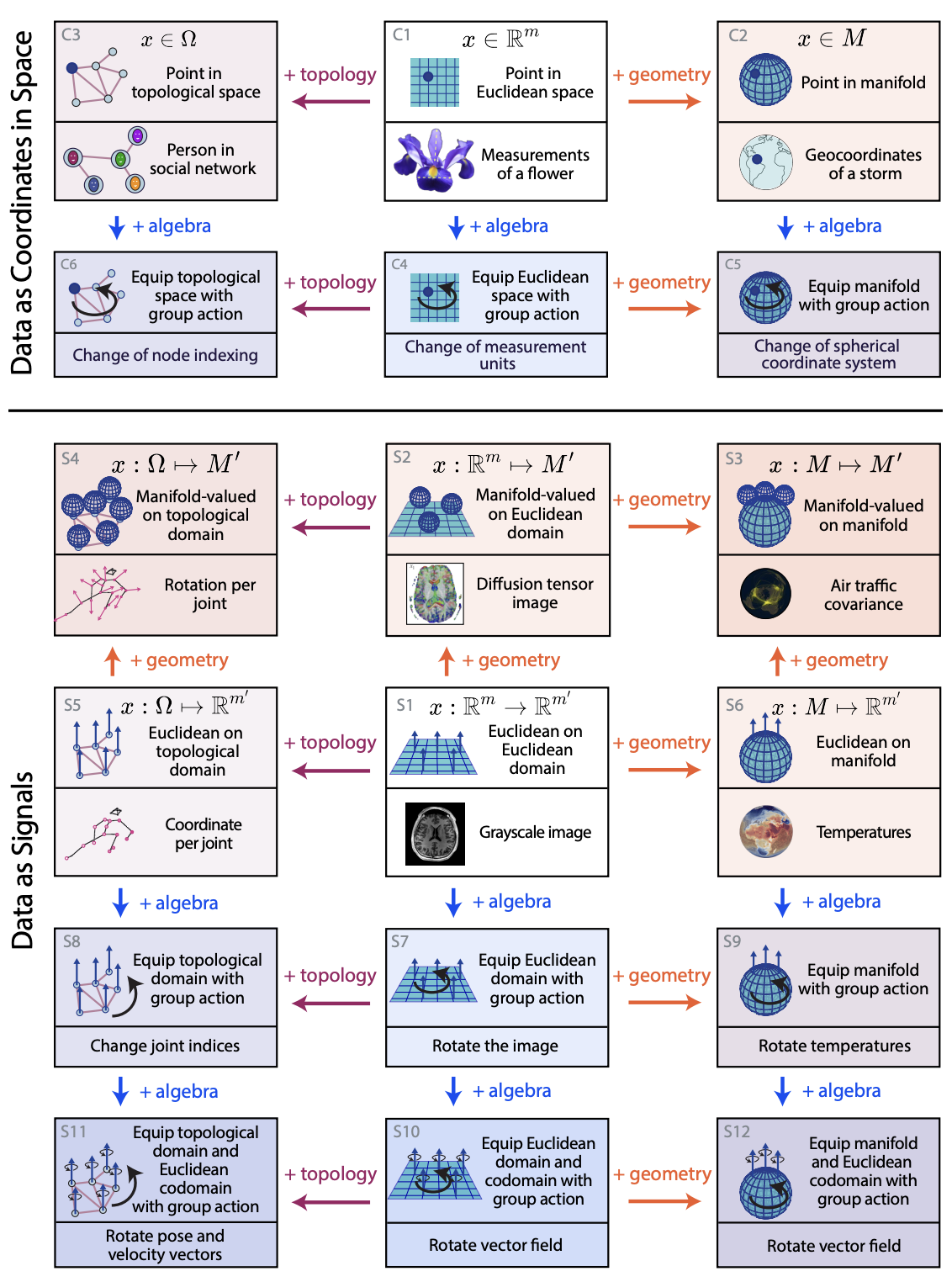
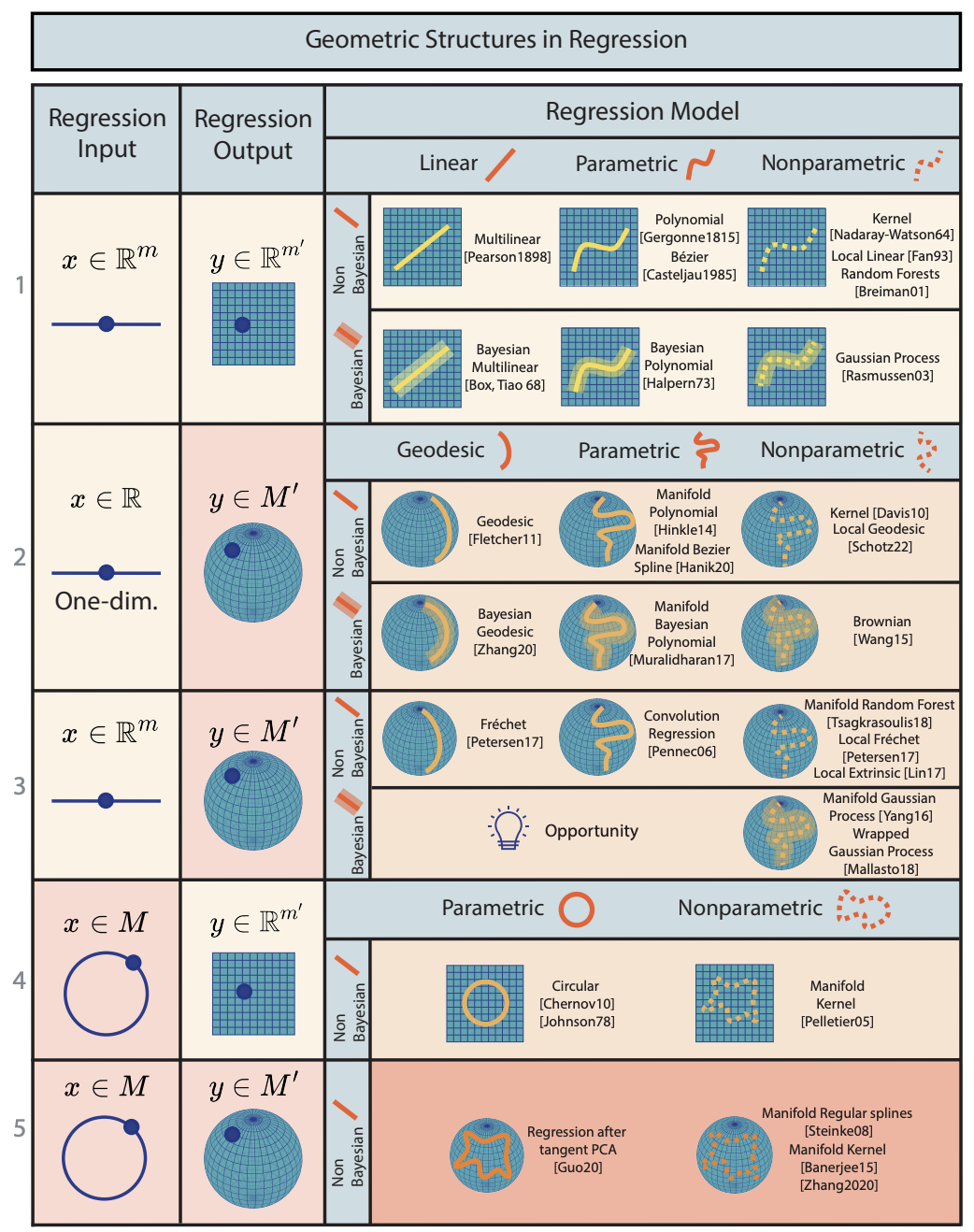
Johan Mathe*, Sophia Sanborn*, Mathilde Papillon*, Domas Buracas, Hansen J Lillemark, Christian Shewmake, Abby Bertics, Xavier Pennec, Nina Miolane Machine Learning: Science and Technology, 2025 The enduring legacy of Euclidean geometry underpins classical machine learning, which, for decades, has been primarily developed for data lying in Euclidean space. Yet, modern machine learning increasingly encounters richly structured data that is inherently non-Euclidean. This data can exhibit intricate geometric, topological and algebraic structure: from the geometry of the curvature of space-time, to topologically complex interactions between neurons in the brain, to the algebraic transformations describing symmetries of physical systems. Extracting knowledge from such non-Euclidean data necessitates a broader mathematical perspective. Echoing the 19th-century revolutions that gave rise to non-Euclidean geometry, an emerging line of research is redefining modern machine learning with non-Euclidean structures. Its goal: generalizing classical methods to unconventional data types with geometry, topology, and algebra. In this review, we provide an accessible gateway to this fast-growing field and propose a graphical taxonomy that integrates recent advances into an intuitive unified framework. We subsequently extract insights into current challenges and highlight exciting opportunities for future development in this field. |
|
Simon Mataigne, Johan Mathe, Sophia Sanborn, Christopher Hillar, Nina Miolane NeurIPS, 2024 An important problem in signal processing and deep learning is to achieve invariance to nuisance factors not relevant for the task. Since many of these factors are describable as the action of a group \( G \) (e.g., rotations, translations, scalings), we want methods to be \( G \)-invariant. The \( G \)-Bispectrum extracts every characteristic of a given signal up to group action: for example, the shape of an object in an image, but not its orientation. Consequently, the \( G \)-Bispectrum has been incorporated into deep neural network architectures as a computational primitive for \( G \)-invariance—akin to a pooling mechanism, but with greater selectivity and robustness. However, the computational cost of the \( G \)-Bispectrum \(\mathcal{O}(|G|^2)\), with \( |G| \) the size of the group, has limited its widespread adoption. Here, we show that the \( G \)-Bispectrum computation contains redundancies that can be reduced into a selective G-Bispectrum with \(\mathcal{O}(|G|)\) complexity. We prove desirable mathematical properties of the selective \( G \)-Bispectrum and demonstrate how its integration in neural networks enhances accuracy and robustness compared to traditional approaches, while enjoying considerable speed-ups compared to the full \( G \)-Bispectrum. |
|
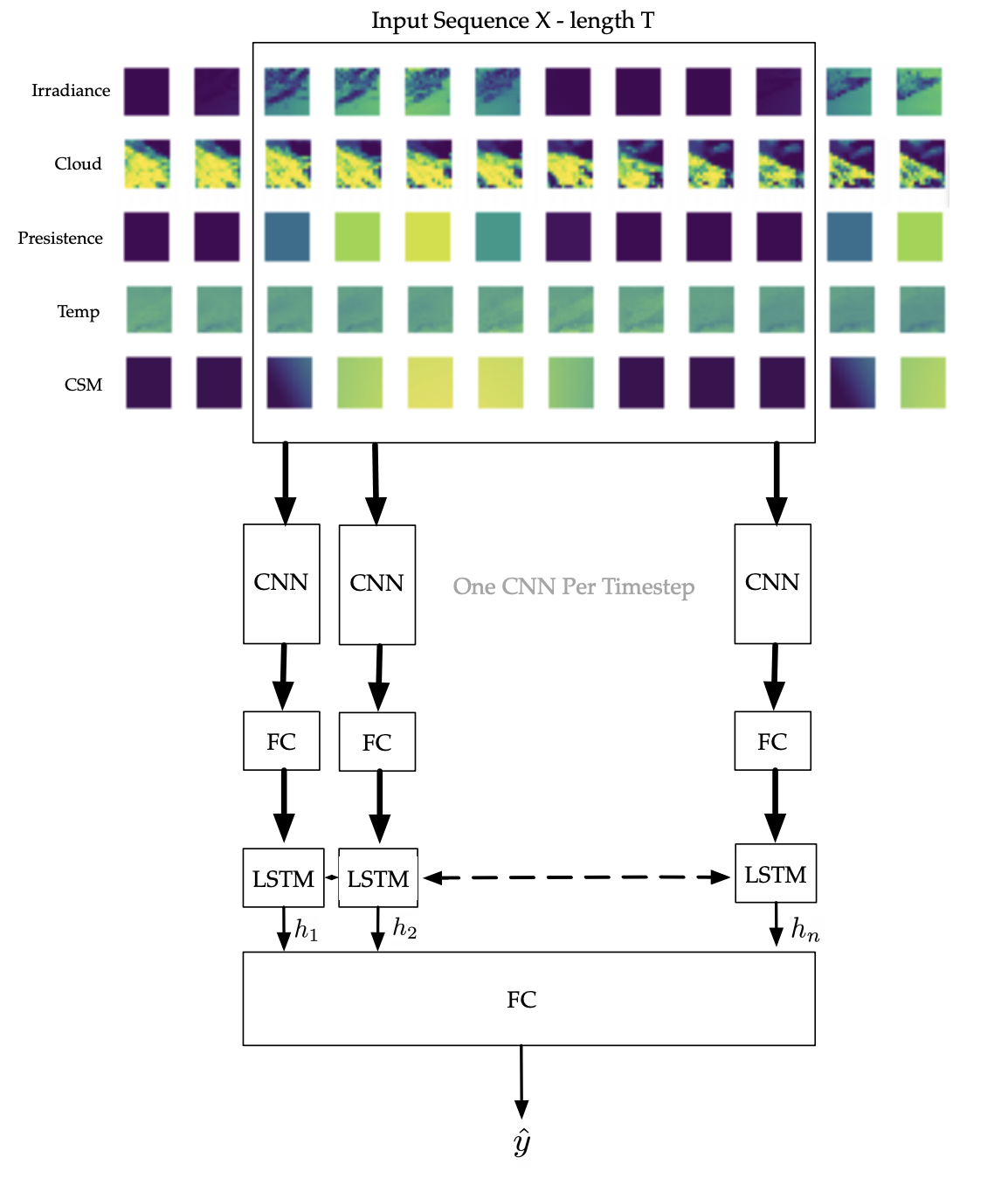
Johan Mathe, Nina Miolane, Nicolas Sebastien, Jeremie Lequeux, ICML Workshop on Climate Change AI, 2019 Photovoltaic (PV) power generation has emerged as one of the lead renewable energy sources. Yet, its production is characterized by high uncertainty, being dependent on weather conditions like solar irradiance and temperature. Predicting PV production, even in the 24 hour forecast, remains a challenge and leads energy providers to keep idle - often carbon emitting - plants. In this paper we introduce a Long-Term Recurrent Convolutional Network using Numerical Weather Predictions (NWP) to predict, in turn, PV production in the 24 hour and 48 hour forecast horizons. This network architecture fully leverages both temporal and spatial weather data, sampled over the whole geographical area of interest. We train our model on a NWP dataset from the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) to predict spatially aggregated PV production in Germany. We compare its performance to the persistence model and to state-of-the-art methods. |
|
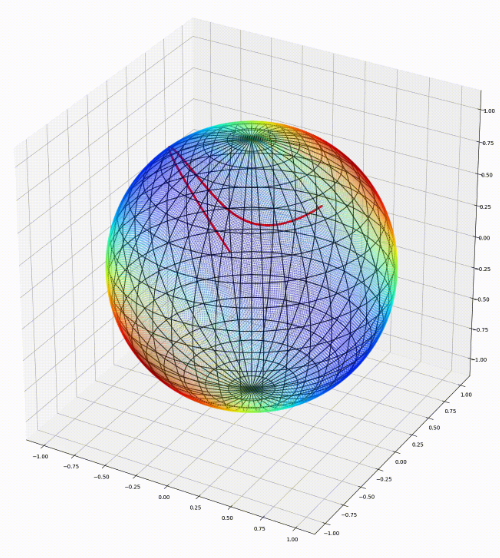
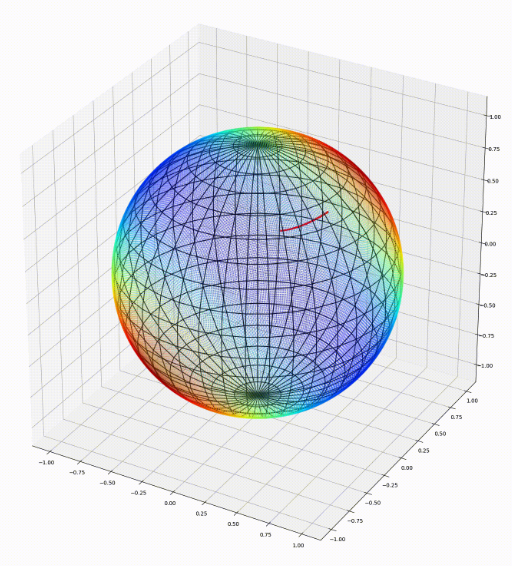
Nina Miolane, Johan Mathe, Claire Donnat, Mikael Jorda, Xavier Pennec, JMLR, 2020 project page A python package that performs computations on manifolds such as hyperspheres, hyperbolic spaces, spaces of symmetric positive definite matrices and Lie groups of transformations. |
|
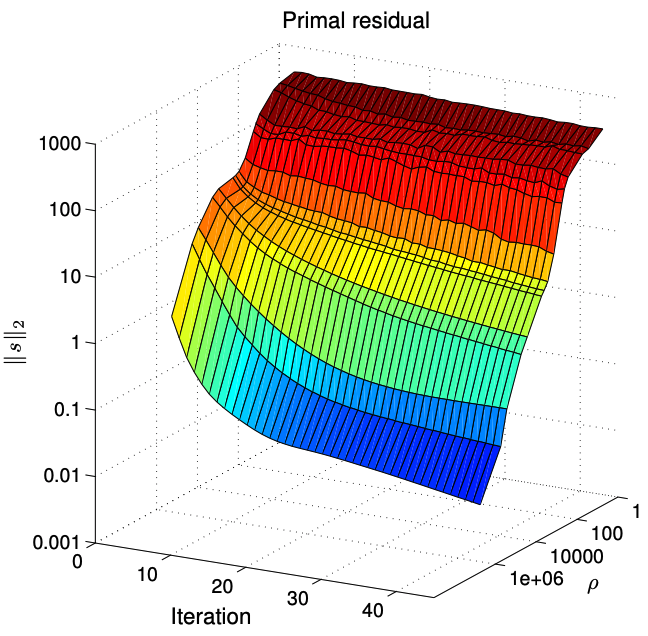
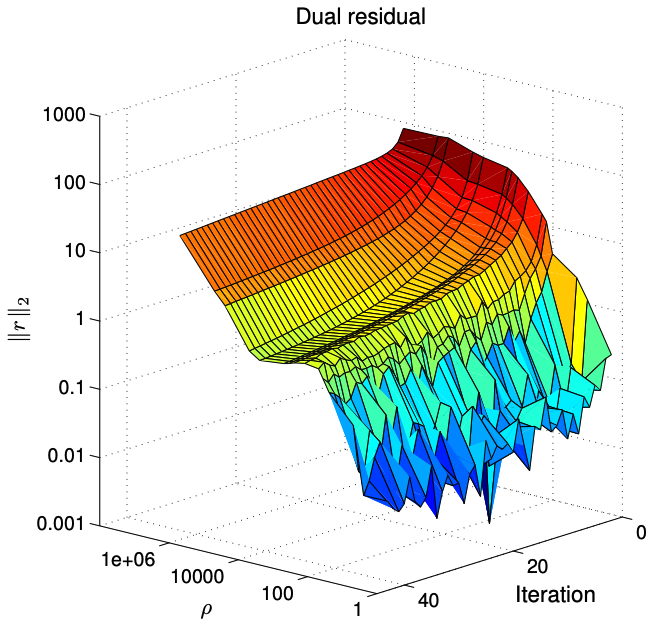
Johan Mathe I implemented the Alternate Direction Method of Multipliers (ADMM) global consensus algorithm with the MapReduce framework and compare the resulting performance with another distributed optimization technique. We will also investigate various caveats with this implementation. More recently I implemented a version of ADMM for keras. |
|
|
|
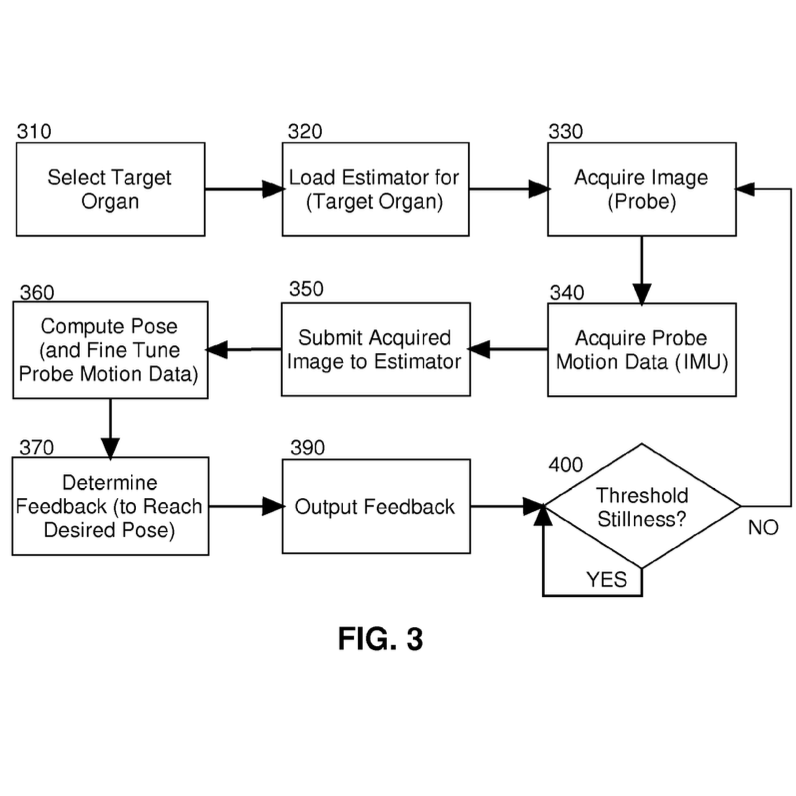
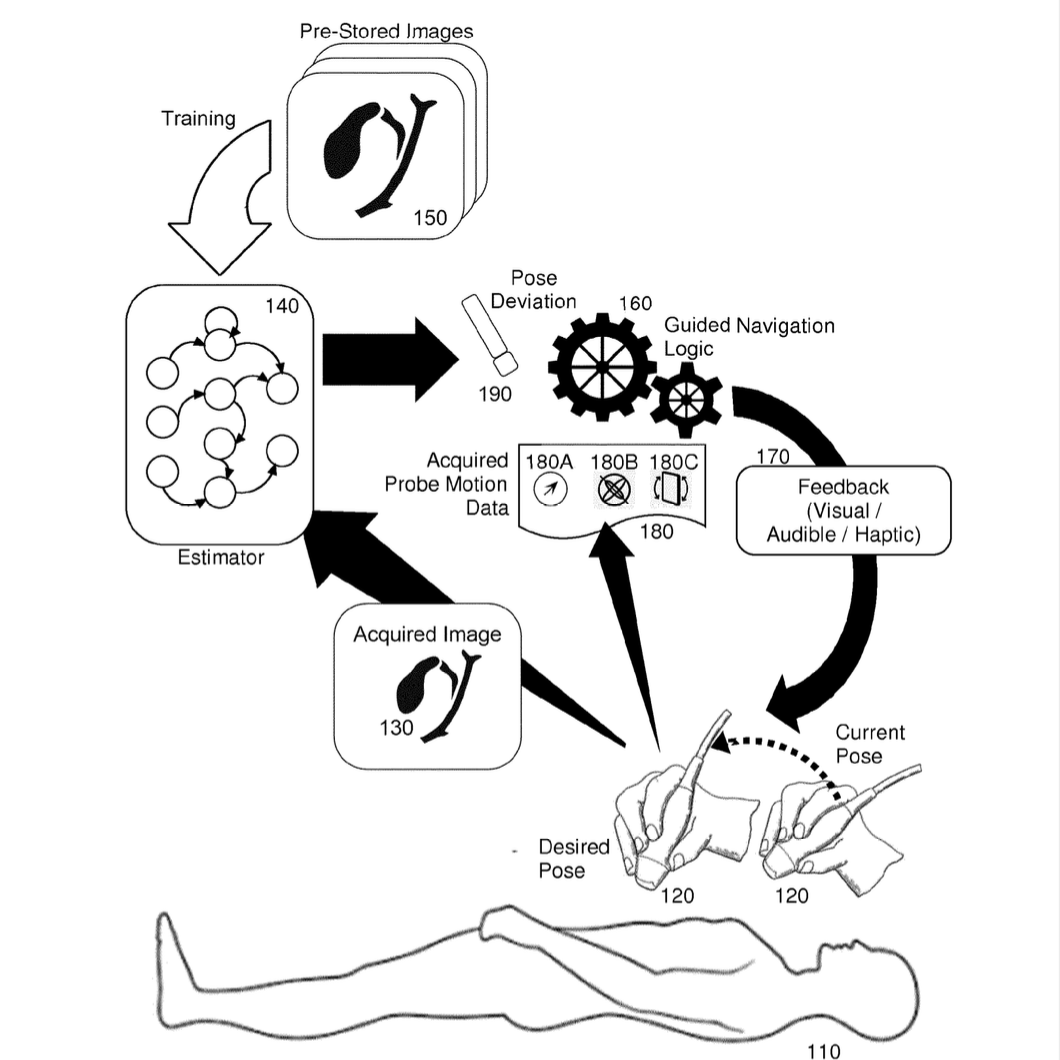
Charles Cadieu, Ha Hong, Kilian Koepsell, Johan Mathe, Martin Wojtczyk Embodiments of the invention provide for the guided navigation of an ultrasound probe. In an embodiment of the invention, an ultrasound navigation assistance method includes acquiring an image by an ultrasound probe of a target organ of a body. The method also includes processing the image in connection with an estimator such as a neural network. The processing in turn determines a deviation of a contemporaneous pose evident from the acquired image from an optimal pose of the ultrasound probe for imaging the target organ. Finally, the method includes presenting the computed deviation to an end user operator of the ultrasound probe. |
|
|
|
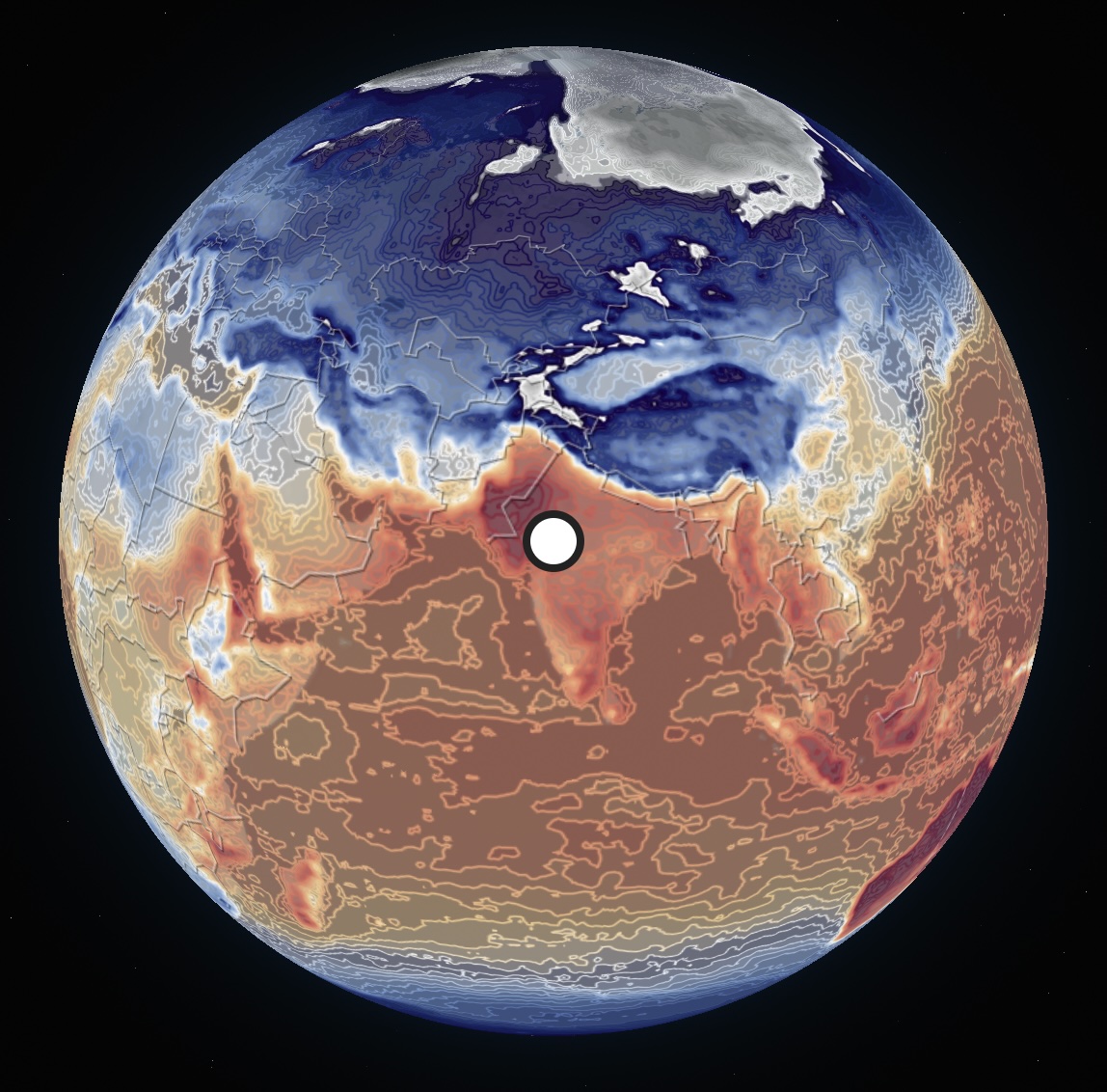
Atmo builds AI-enabled hardware–software systems for weather forecasting at city, state, and national scales. Under Johan's leadership, Atmo became the first private company to deploy AI weather models operationally for entire nations, including the Philippines—one of the regions most exposed to typhoons and climate-driven extreme weather. These systems are used daily by governments and defense agencies to support real-world decision-making, marking one of the earliest large-scale deployments of AI explicitly aimed at climate risk mitigation. |
|
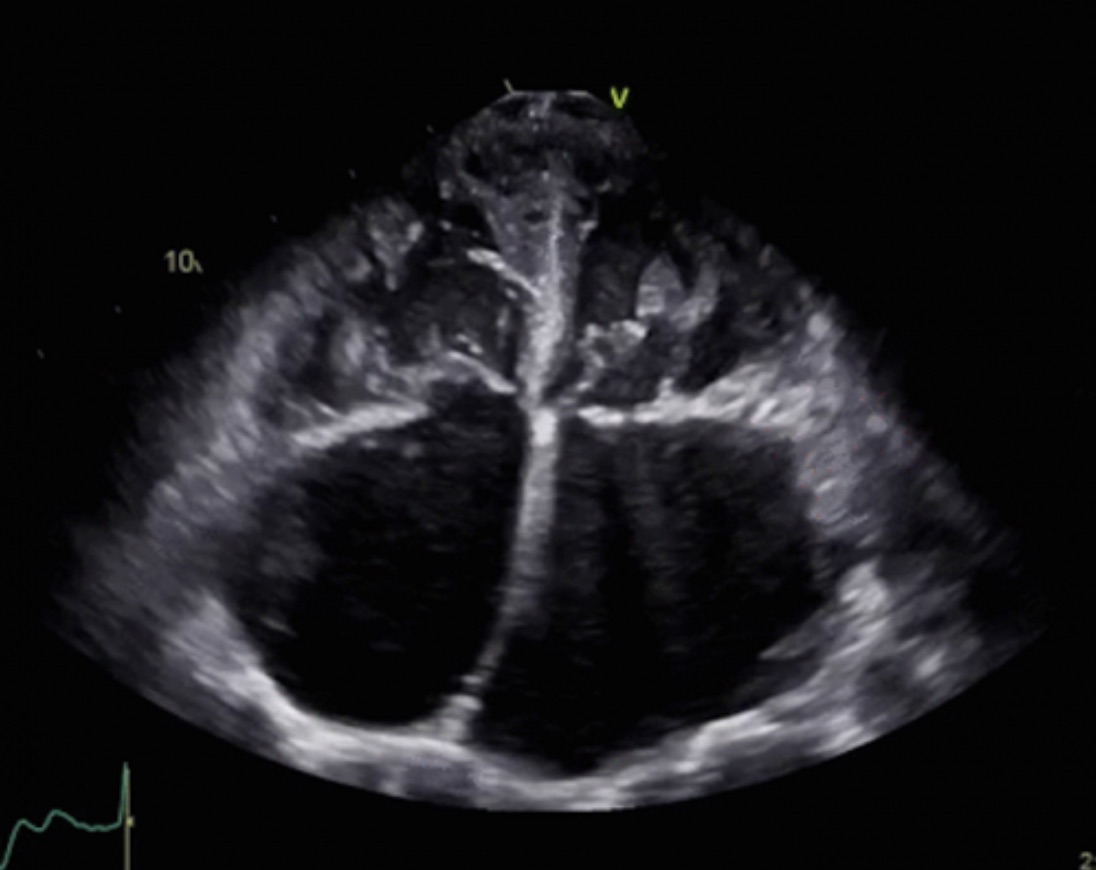
Johan was part of the founding team at Caption Health, where he designed early guidance and diagnostic algorithms for AI-assisted ultrasound. His work focused in part on Rheumatic Heart Disease, collaborating closely with echocardiographers and pediatricians from the American Society of Echocardiography. As part of this effort, he traveled to Kenya to help deploy AI-driven diagnostics in remote villages, enabling early detection for children with limited access to specialist care. Additional context is covered in Jack's newsletter. |
|
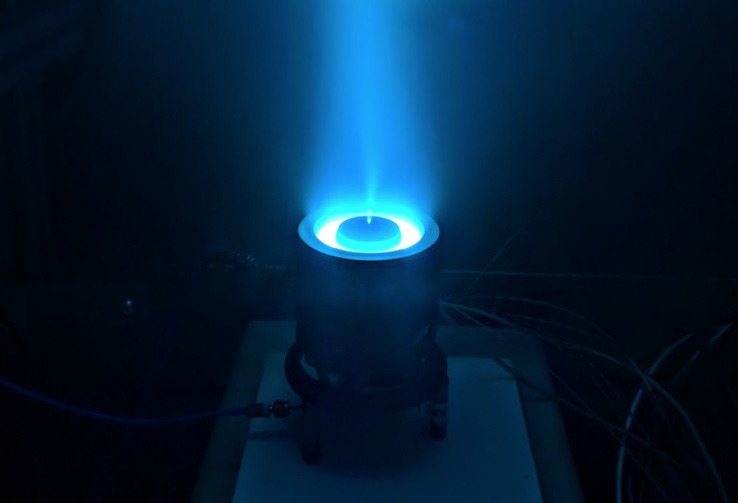
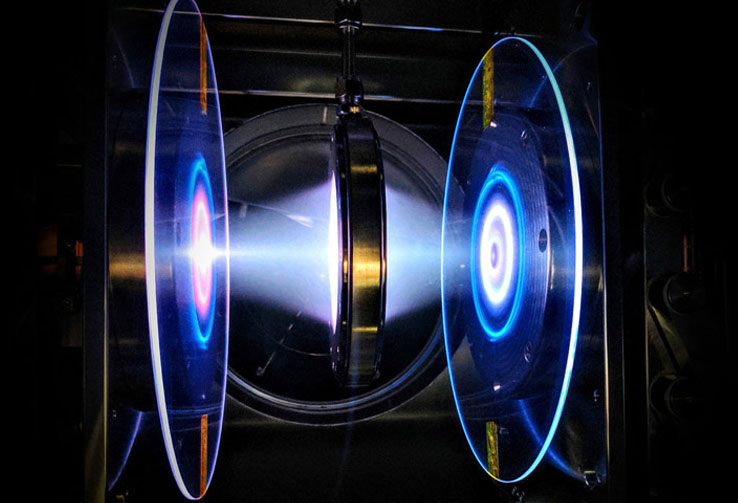
At Apollo Fusion, Johan developed black-box optimization methods to improve the performance of plasma-based propulsion systems using reactor-in-the-loop experimentation. These performance gains directly informed the development of improved Hall-effect thrusters. He also led the design of the Power Processing Unit, responsible for converting spacecraft bus power into the precise electrical signals required to drive the thruster. |
 
|
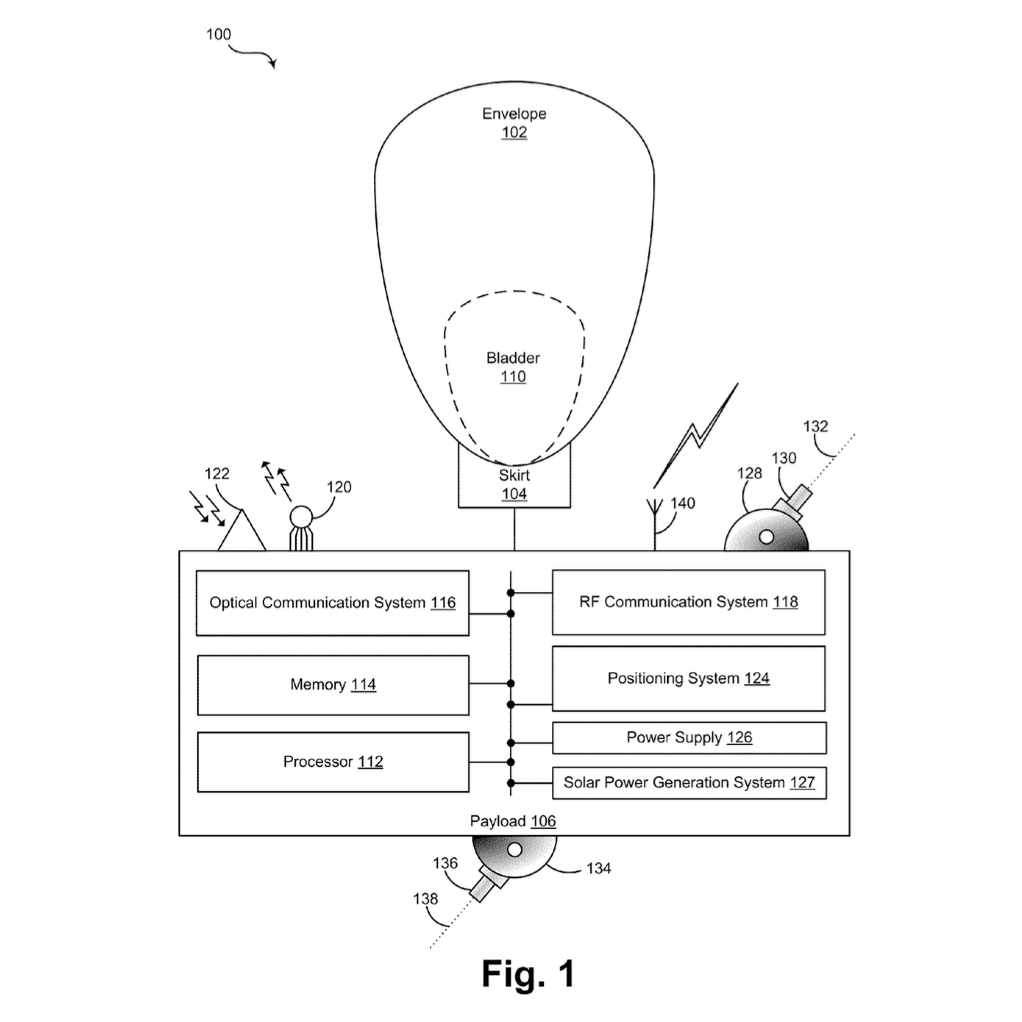
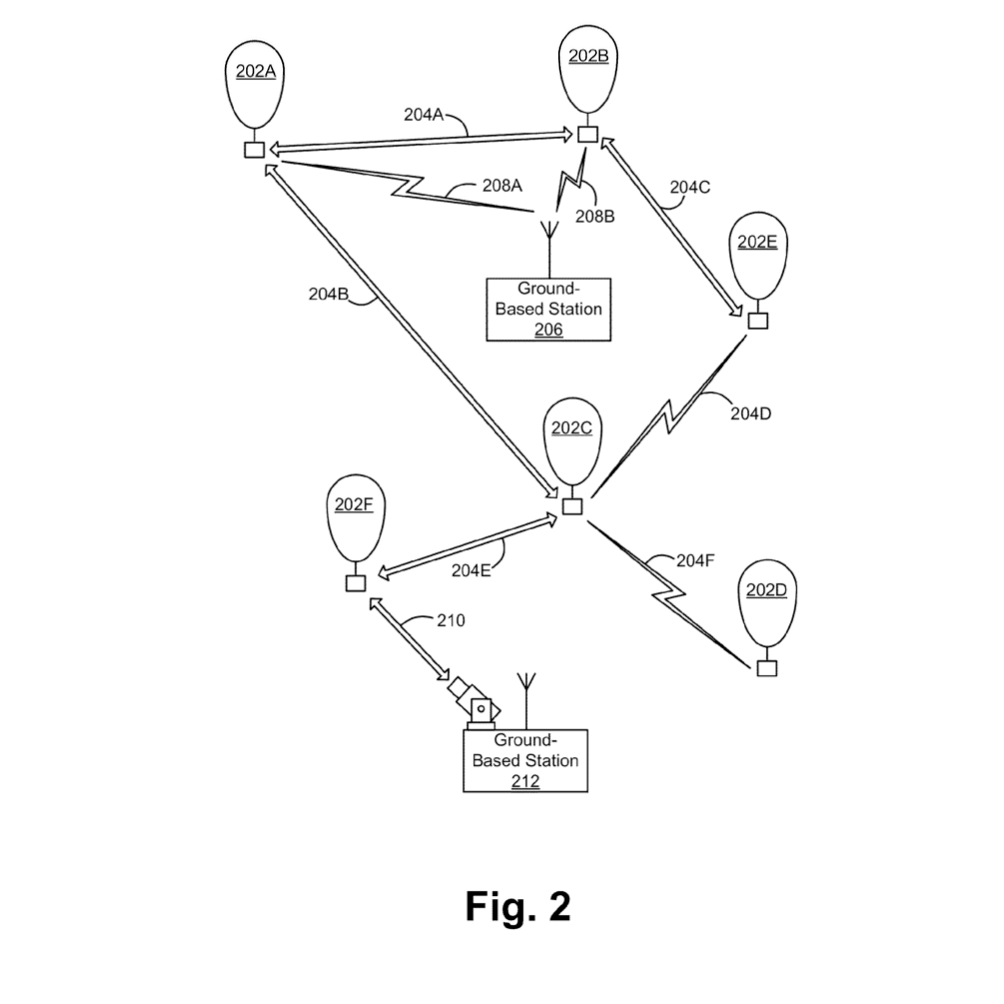
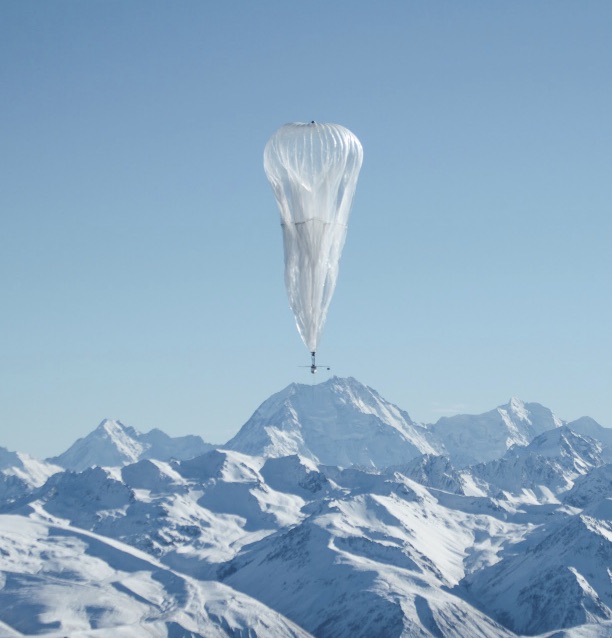
At Google X and Project Loon, Johan designed some of the original guidance and navigation algorithms for stratospheric balloons. This work marked his first deep engagement with atmospheric and wind data at scale, focusing on optimal control, path planning, and explore–exploit strategies that enabled unprecedented balloon steering performance. The navigation system has been covered in detail by MIT Technology Review and The Verge. |

|
Earlier at Google, Johan worked on large-scale distributed systems, contributing to the Google File System and its successor, Colossus. He later worked on the Census library and helped design the first version of what became gRPC, Google's widely adopted remote procedure call framework. |